马克思主义的简答题
本文共 651 字,大约阅读时间需要 2 分钟。
-
马克思主义的含义:
马克思主义是由马克思,恩格斯创立的,为它们的后继者所发展,以批判资本主义,建设社会主义和实现共产主义为目标的科学理论体系,是关于无产阶级和人类解放的科学- 三大理论体系: 马克思主义哲学,马克思主义政治经济学,科学社会主义 联系: 马克思主义各个组成部分 ,是一个具有内在逻辑联系的科学体系,其中: 马克思主义哲学: 是科学的世界观和方法论 政治经济学 : 是马克思主义的理论基础 科学社会主义::处于马克思主义核心地位 这三者相互渗透,相互补充,构成统一的马克思主义 学说
 答案: C 三大理论体系的来源以及代表人物 马克思主义哲学: 德国古典哲学 ——黑格尔,费尔巴哈 马克思主义政治经济学 : 英国古典经济学 ——亚当斯密 ,大卫·李嘉图 科学社会主义: 英法两国的空想社会主义学说 —— 圣西门,傅立叶 欧文
答案: C 三大理论体系的来源以及代表人物 马克思主义哲学: 德国古典哲学 ——黑格尔,费尔巴哈 马克思主义政治经济学 : 英国古典经济学 ——亚当斯密 ,大卫·李嘉图 科学社会主义: 英法两国的空想社会主义学说 —— 圣西门,傅立叶 欧文  答案 : C 简述马克思主义对德国古典哲学,英国古典经济学,和英法两国的空想社会主义学说的发展: 马克思,恩格斯吸收了黑格尔辩证法中的合理思想和费尔巴哈唯物主义的基本思想,创立了辩证唯物主义和历史唯物主义 马克思,恩格斯吸取了英国古典经济学家的劳动价值论等合理思想,创立了剩余价值学说 马克思,恩格斯批判的吸收了空想社会主义学说的积极成果,创立了科学社会主义理论
答案 : C 简述马克思主义对德国古典哲学,英国古典经济学,和英法两国的空想社会主义学说的发展: 马克思,恩格斯吸收了黑格尔辩证法中的合理思想和费尔巴哈唯物主义的基本思想,创立了辩证唯物主义和历史唯物主义 马克思,恩格斯吸取了英国古典经济学家的劳动价值论等合理思想,创立了剩余价值学说 马克思,恩格斯批判的吸收了空想社会主义学说的积极成果,创立了科学社会主义理论
- 三大理论体系: 马克思主义哲学,马克思主义政治经济学,科学社会主义 联系: 马克思主义各个组成部分 ,是一个具有内在逻辑联系的科学体系,其中: 马克思主义哲学: 是科学的世界观和方法论 政治经济学 : 是马克思主义的理论基础 科学社会主义::处于马克思主义核心地位 这三者相互渗透,相互补充,构成统一的马克思主义 学说













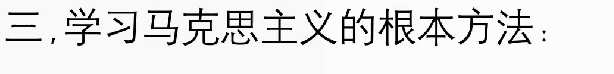 理论联系实际,就是把马克思主义的基本原理作为指导,去观察和分析社会实际、工作实际和思想实际。要做到理论联系实际。,在实际工作中反对经验主义和教条主义两种倾向。
理论联系实际,就是把马克思主义的基本原理作为指导,去观察和分析社会实际、工作实际和思想实际。要做到理论联系实际。,在实际工作中反对经验主义和教条主义两种倾向。  学习马克思主义的目的
学习马克思主义的目的 


转载地址:http://ifvv.baihongyu.com/
你可能感兴趣的文章
NIFI大数据进阶_实时同步MySql的数据到Hive中去_可增量同步_实时监控MySql数据库变化_操作方法说明_01---大数据之Nifi工作笔记0033
查看>>
NIFI大数据进阶_离线同步MySql数据到HDFS_01_实际操作---大数据之Nifi工作笔记0029
查看>>
NIFI大数据进阶_离线同步MySql数据到HDFS_02_实际操作_splitjson处理器_puthdfs处理器_querydatabasetable处理器---大数据之Nifi工作笔记0030
查看>>
NIFI大数据进阶_离线同步MySql数据到HDFS_说明操作步骤---大数据之Nifi工作笔记0028
查看>>
NIFI大数据进阶_连接与关系_设置数据流负载均衡_设置背压_设置展现弯曲_介绍以及实际操作---大数据之Nifi工作笔记0027
查看>>
NIFI数据库同步_多表_特定表同时同步_实际操作_MySqlToMysql_可推广到其他数据库_Postgresql_Hbase_SqlServer等----大数据之Nifi工作笔记0053
查看>>
NIFI汉化_替换logo_二次开发_Idea编译NIFI最新源码_详细过程记录_全解析_Maven编译NIFI避坑指南001---大数据之Nifi工作笔记0068
查看>>
NIFI汉化_替换logo_二次开发_Idea编译NIFI最新源码_详细过程记录_全解析_Maven编译NIFI避坑指南002---大数据之Nifi工作笔记0069
查看>>
NIFI集群_内存溢出_CPU占用100%修复_GC overhead limit exceeded_NIFI: out of memory error ---大数据之Nifi工作笔记0017
查看>>
NIFI集群_队列Queue中数据无法清空_清除队列数据报错_无法删除queue_解决_集群中机器交替重启删除---大数据之Nifi工作笔记0061
查看>>
NIH发布包含10600张CT图像数据库 为AI算法测试铺路
查看>>
Nim教程【十二】
查看>>
Nim游戏
查看>>
NIO ByteBuffer实现原理
查看>>
Nio ByteBuffer组件读写指针切换原理与常用方法
查看>>
NIO Selector实现原理
查看>>
nio 中channel和buffer的基本使用
查看>>
NIO三大组件基础知识
查看>>
NIO与零拷贝和AIO
查看>>
NIO同步网络编程
查看>>